Thameslink

Thameslink is a fifty-station line in the British railway system running 225 km (140 miles) north to south across London from Bedford to Brighton through Snow Hill tunnel. It is a significant commuter route and serves the airports at London Gatwick and London Luton. There are well over 40 million passenger journeys on the system annually.[citation needed] It incorporates the Brighton Main Line and part of the Midland Main Line.
Upon the privatisation of British Rail the operation of Thameslink services was franchised to a subsidiary Govia, the train operating company ‘Thameslink’. From 1 April 2006, it was taken over by First Capital Connect along with other services previously operated by wagn. The branding of most trains, stations, and signs has been changed to reflect the name of the new company, but City Thameslink, King’s Cross Thameslink and West Hampstead Thameslink stations retain the word ‘Thameslink’ in their names, since the suffix refers to the Thameslink route itself.
Contents
History
The Snow Hill tunnel was re-opened to passengers after 50 years in 1988 and the Thameslink network in May 1990. Prior to this, the northern section was run as the "Bedpan" service from Bedford to London St Pancras, using the Midland Main Line. Some services ran into the old Widened Lines to London Moorgate. From the south, services terminated at Holborn Viaduct.
Running from north to south the central London stations are: Kings Cross Thameslink on Pentonville Road (close to King's Cross railway station and connected to Kings Cross St. Pancras tube station via foot tunnel); Farringdon station, which links into the London Underground’s Circle and Metropolitan lines; City Thameslink (formerly St. Paul’s Thameslink station — the name was changed to avoid confusion with St. Paul's tube station which is a considerable distance away), which replaced the demolished Holborn Viaduct; Blackfriars, which links to a number of other franchises and the District and Circle lines on the Underground; and London Bridge, which also links to a number of other lines.
In the south there are two branches. The "main line" runs through London Bridge to East Croydon, then to Brighton. A second branch has a more convoluted history.
In its first incarnation, trains went down via Bromley to Orpington and Sevenoaks. Some time after that, the non-Brighton trains ran via Elephant and Castle and Streatham to West Croydon.[citation needed] Although this route, still used by other train services, comes close to the "main line", it never relinks with it. After West Croydon the line ran through Carshalton Beeches to Sutton then to Epsom, Leatherhead, Effingham Junction and finally terminating at Guildford.[citation needed] However this route crossed the commuter networks of what were to become several different rail companies and the onset of rail privatisation made the route increasingly difficult to maintain. Around 1994 the second branch was cut back to West Croydon.[citation needed] Then around 1995 a major overhaul occurred when the route was changed completely. West Croydon was abandoned by Thameslink and instead a new route to Sutton was opened up over existing track through Mitcham Junction with the line then continuing on a loop up to Wimbledon and then rejoining itself south of Streatham.
The proposed Crossrail project would operate a similar cross-London service from the east to the west, although unlike Thameslink it does not involve re-opening old tunnels.
Rolling stock
The Thameslink rolling stock is composed of 74 Class 319 trains built by BREL between 1987 and 1990. These are electrically powered dual-voltage four-car units rated to hold either 289, 308 or 319 passengers.[citation needed] They use 25 kV AC overhead power north of Farringdon and 750 V DC third rail to the south.
Thameslink Programme (Thameslink 2000)
Since 1991, British Rail (followed by Railtrack, then Network Rail) have been developing proposals to expand and upgrade the Thameslink network in light of the high patronage experienced by operators on the route, particularly today. The project is known as the Thameslink Programme. After a complex, prolonged and frustrating planning process (which officialy began in November 1997), Network Rail (the body currently responsible for developing and executing the project) was finally given planning permission and legal powers on 18th October 2006.[1] However, the money needed to pay for it (£3.1 billion at 2001 prices, £3.5 billion at current nominal prices) has not yet been secured, and the Department for Transport stated that a final decision on funding would be made by summer 2007.[2]
Stations served by Thameslink
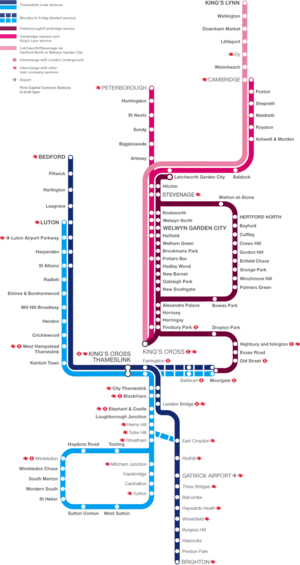
Below is a list of the stations on the Thameslink route, starting from the north:
Bedford - Flitwick - Harlington - Leagrave - Luton - Luton Airport Parkway - Harpenden - St Albans - Radlett - Elstree & Borehamwood - Mill Hill Broadway - Hendon - Cricklewood - West Hampstead Thameslink - Kentish Town - King’s Cross Thameslink - Farringdon
A short branch leaves the main line, going to:
The main line continues south to:
Again, the line splits, with one branch continuing south to:
London Bridge - East Croydon - Redhill - Gatwick Airport - Three Bridges - Balcombe - Haywards Heath - Wivelsfield - Burgess Hill - Hassocks - Preston Park - Brighton
The other branch goes to:
Elephant & Castle - Loughborough Junction - Herne Hill - Tulse Hill - Streatham
The line then splits into a loop as follows:
Tooting - Haydons Road - Wimbledon - Wimbledon Chase - South Merton - Morden South - St. Helier - Sutton Common - West Sutton - Sutton - Carshalton - Hackbridge - Mitcham Junction - Streatham
References
- ↑ Network Rail (2006-10-18). THE £3.5BN THAMESLINK PROJECT CLEARS MAJOR HURDLE. Retrieved on 2006-11-20.
- ↑ BBC News (2006-10-18). 'Landmark' ruling for Thameslink. Retrieved on 2006-11-20.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Thameslink |
- Official Thameslink Programme website - by Network Rail
- Thameslink 2000 Public Inquiry 2005 - official website for the second public inquiry
- Strategic Rail Authority Strategic Plan, 30 January 2003, page 101 and route descriptions page 27.
- alwaystouchout.com - information and news on the Thameslink Programme
- Department for Transport press release announcing First Group’s successful bid

