Middleton Railway
The Middleton Steam Railway is the world's oldest working railway. It was founded in 1758 and is now a heritage railway run by enthusiasts.
The railway operates passenger services at weekends and on public holidays over approximately 1 mile of track between its headquarters at Moor Road, Hunslet, Leeds, and Park Halt on the outskirts of Middleton Park.
Origins
The Middleton Steam Railway was the first railway to be authorised by Act of Parliament in 1758. It was built to a gauge of 4 ft 1 in to carry coal from the pits owned by Charles Brandling to Leeds. Not all the land belonged to Brandling and the Act gave him power to obtain wayleave. Otherwise the line was privately financed and operated, initially as a wagonway using horse-drawn vehicles. Around 1807 the wooden tracks began to be replaced with edge rails.
Introduction of steam
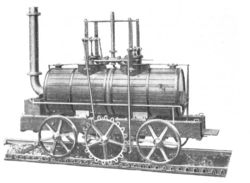
In 1812 the Middleton Steam Railway became the first railway to commercially use steam locomotives. John Blenkinsop the colliery's viewer, or manager, decided that an engine light enough not to break the track would not have sufficient adhesion. Accordingly he relaid the track on one side with a toothed rail, which he patented in 1811, and approached Matthew Murray of Fenton, Murray and Wood to design a locomotive with a pinion which would mesh with it. Murray's design was based on Richard Trevithick's Catch me who can, adapted to use Blenkinsop's rack and pinion system, and was called The Salamanca. The loco was the first to use two cylinders. These drove the pinions through cranks which were at right angles, so that it would start wherever it came to rest.
The line thus entered the history books, in 1812, for it was first to operate successfully, and with three more locos built later, remained in use for another twenty years. In 1881 the railway was converted to 4 ft 8½ in (1435 mm) standard gauge.
Preservation
In June 1960, the Middleton Steam Railway became the first standard-gauge railway to be taken over and operated by unpaid volunteers. Passenger services were initially only operated for one week, using an ex Swansea and Mumbles Railway double deck carriage. However, the volunteers of the Middleton Railway operated a freight service until 1983.
Regular operation of passenger services began in 1969.
The Middleton Steam Railway is home to a representative selection of locomotives built by the famous Leeds manufacturers of John Fowler, Hudswell Clarke, Hunslet Engine Company, Kitson & Co. and Manning Wardle. The locomotives include "Sir Berkeley", which was featured in the 1968 BBC TV version of "The Railway Children". The locomotive is owned by the Vintage Carriages Trust of Ingrow near Keighley.
Reference
- Ransom, P.J.G., (1990) The Victorian Railway and How It Evolved, London: Heinemann
External links
- The Middleton Railway
- Map sources for Middleton Railway