Korea Train Express
{{#if:한국고속철도韓國高速鐵道|
{{#switch: |n |north |dprk |nk={{#if:| Korea Train Express | |
|---|---|
 KTX train at Seoul Station | |
| Korean name | |
| Chosŏn'gŭl: | 한국고속철도 |
| Hanja: | 韓國高速鐵道 |
| McCune-Reischauer: | Han-guk Kosok Ch'ŏlto |
| Revised Romanization: | Han-guk Gosok Cheoldo |
|s |south |rok |sk
| #default = <th style="background:#ccf; border-bottom:1px solid; color:" width=" Korea Train Express (KTX) is South Korea's high-speed rail system. It is operated by Korail. The train's technology is largely based on the French TGV system, and features top speeds of 300 km/h or more. On December 16, 2004, the Korean-made HSR-350x had an experimental run at 352.4 kilometers per hour.[1]
History
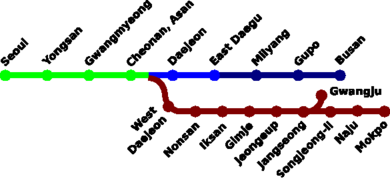
After 12 years of construction, the Gyeongbu Line (connecting Seoul to Busan via Daejeon and Daegu) and the Honam Line (Seoul to Gwangju and Mokpo) opened on March 31, 2004. Using high-speed track for only a part of the distance (Seoul-Daegu), the new line cuts travel time between Seoul and Busan from 4 hours 10 minutes with the Saemaul-ho to 2 hours 40 minutes, and between Seoul and Mokpo from 4 hours 42 minutes to 2 hours 58 minutes.[2] A further improvement to a 1 hour 56 minutes on the Gyeongbu Line is expected in 2008, when the train shifts to run fully on high-speed tracks.
In all, 46 trains will be built: twelve in France by Alstom, the remaining in South Korea by ROTEM. The tracks were built with the technical help of SNCF technicians.
Future
Construction of the second phase linking Daegu and Gyeongju to Busan started in June 2002 and is expected to be complete by 2010. High-speed track for the section from Osong to Gwangju and Mokpo is also planned, with a tentative target date of 2017.[3] A spur line from Seoul to Gangneung, on the northeast coast, is under consideration, and is linked to the Korean bid for the 2014 Winter Olympics[citation needed].
Ridership
When introduced in April 2004, KTX ridership was an average of 70,900 passengers per day, 70% below initial expectations. While earning an operational profit of about 2.1 billion won per day, this amount was insufficient to service the loans, as the construction cost grew from an initial estimate of 5 trillion to an actual 18 trillion Korean won (approx. 5 billion to 18 billion US dollars). On January 14, 2005, Prime Minister Lee Hai Chan stated that KTX was a political failure.
Ridership has, however, slowly been increasing. On January 9, 2006, Korail reported that average daily ridership in December 2005 had reached 104,600, an increase of almost 50%, with daily operating profit up to 2.8 billion won and financial breakeven expected by early 2007.[4]
According to the investigation of Grand National Party in 2006, KTX broke down 160 times in three years.[5] Obtaining spare parts for the KTX from French suppliers can be a time-consuming process.
See also
References
- ↑ HSR350x Tops 350km/h. KITECH (2005-05-31). Retrieved on 2006-12-15.
- ↑ KTX Overview (Korean). KTX website. Retrieved on 2007-01-18.
- ↑ Seoul-Mokpo Bullet Train to Debut in 2017. The Korea Times (2005-12-22). Retrieved on 2006-12-15.
- ↑ KTX Tops 100,000 Passengers Per Day. The Korea Times (2006-01-09). Retrieved on 2006-12-15.
- ↑ KTX 고장나면 다른 차량 부품 떼어 "땜질" (Korean). Prime Business Journal (2006-10-13). Retrieved on 2006-12-15.
External links
- Korea Train eXpress
- Route Map
- JRTR Issue 40: Transportation Revolution, the Korean High-Speed Railway
| High-speed trains | |
|---|---|
| Acela Express • Alfa Pendular • AVE • ETR 500 • Eurostar • InterCityExpress • JR-Maglev MLX01 • HST • Korea Train Express • Magnetic levitation trains • Pendolino • Shinkansen • TGV • Thalys • THSR • Transrapid • Treno Alta Velocità • X 2000 |
es:Korea Train Express fr:Korea Train Express ko:한국고속철도 id:KTX ja:KTX pt:Korea Train Express ro:Korea Train Express zh:韓國高速鐵道