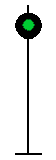User:Dp67/Sandboxes/North American railway signaling
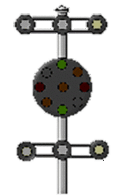 A drawing of a complete B&O style signal head. (Lights Out)
A drawing of a complete B&O style signal head. (Lights Out)
- This article describes the operating procedures of North American railroad signals.
This article will explain some of the aspects of railroad signaling. For a more technical look at how signals actually work, read North American railway signaling.
- The railroad signals of North America can be broken down into three basic types of signals.
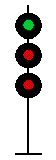
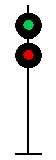
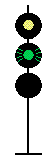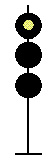
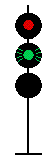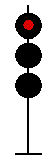
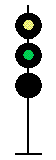
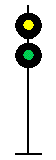
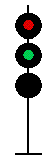
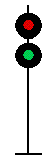
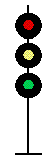
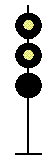
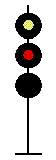
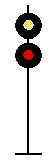
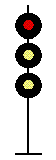
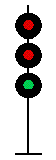
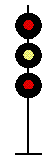
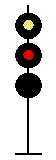
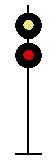
- Color - The 5 colors used are,red, yellow, green, white (used as a modifier) and sometimes blue and purple. Each color of the signal indicates one procedure, Red = stop, yellow (or amber) = caution, green = proceed. White is used as a modifier, for example, a red light would normally mean stop. Adding a white light to the red signal could mean stop and proceed. Or a white light with a green could mean proceed at a restricted speed.
- Position - A single color may be used for all rules whereas the position of the lights describes the proper procedure.
- Color-Position - a combination of the two methods above whereas colors are used in various positions to describe the proper procedure.
Signals and aspects
Note: Images are placed side by side for a clearer perspective on the possible light configurations. Under normal conditions there may only be one or two light trees.
Definitions:
Absolute Block - a block that may be occupied by only one train at a time.
Absolute Signal - a color light, color position light, or semaphore signal without a number plate, "P" marker, APP" marker, "C" marker, or "G" marker, that conveys Stop as its most restrictive aspect. Automatic Block Signal System (ABS)- a series of consecutive blocks whose use is governed by train[-]actuated block signals or by certain conditions affecting the use of a block. Unless so specified, such signals do not authorize the movement of trains.
Block - a track section of defined limits. In signaled territory, a block is the track section between two consecutive block signals governing movements in the same direction. It is also the track section from a block signal to the end of signaled territory.
Block Signal - an absolute or intermediate signal at the entrance to a block that governs the movement of trains using that block.
Color Light Signal - a fixed signal that displays aspects by the color of a light. It may also display aspects by a combination of colored lights.
Color Position Light Signal (CPL) - a fixed signal that displays aspects by the color or position of two or more lights.
Current of Traffic - the movement of trains on a main track, in one direction, as specified by the rules or special instructions.
Direct Traffic Control Block - a block whose use is governed by verbal authority of the train dispatcher.
Fixed Signal - a permanent signal or sign indicating a condition affecting train movement.
Interlocking - an arrangement of interconnected signals and signal appliances for which interlocking rules are in effect. Signals and movement of signal appliances must succeed each other in proper sequence.
Interlocking Signals - fixed signals of an interlocking.
Intermediate Signal - a block signal equipped with either a number plate, a "G" marker, or "P" marker. It conveys Stop and Proceed at Restricted Speed as its most restrictive indication.
Main Track - a track extending through yards and between stations. It is other than an auxiliary track.
Siding - an auxiliary track for meeting or passing trains. It is designated in special instructions.
Traffic Control Signal System (TCS) - a signal system under which opposing and following train movements are authorized and governed� by block signals.
Train - an engine, with or without cars, displaying a marker.
Notes and references
- The Pennsylvania Railroad rules for conducting transportation, October 28, 1956
- The Pennsylvania Railroad rules for conducting transportation, April 28, 1968